Introduction:
Cancer remains one of the most formidable health challenges worldwide. It is characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells, and if not managed, can be fatal. Globally, cancer accounted for nearly 10 million deaths in 2020, making it the second leading cause of death according to the World Health Organization (WHO). In India, the burden of cancer is equally staggering, with over 1.3 million new cases diagnosed annually and nearly 850,000 deaths attributed to the disease in 2020.
Cancer Stem Cells: The Root of the Problem
A significant discovery in the realm of oncology is the identification of cancer stem cells (CSCs). These cells possess the ability to self-renew and differentiate, much like normal stem cells. However, CSCs are particularly insidious as they can drive tumor growth and metastasis. They are also often resistant to conventional therapies, contributing to tumor relapse and poor prognosis.
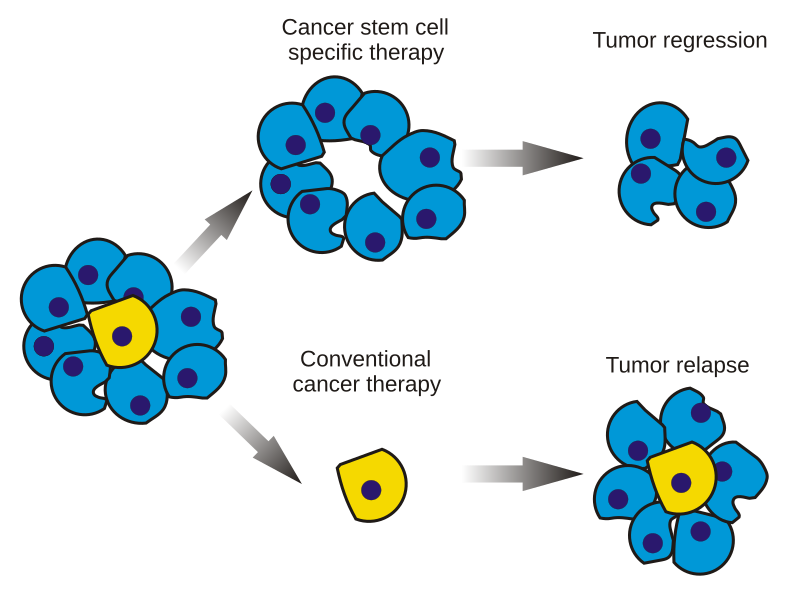
Standard Cancer Treatments and Their Drawbacks
The Standard of Care (SOC) approach to cancer treatment include
- surgery,
- radiation therapy,
- chemotherapy and
- immunotherapy
While these therapies can be effective in targeting and eliminating cancer cells, they are not without significant drawbacks:
1. Surgery: Although it can remove tumors, it is invasive and may not be feasible for all patients, particularly those with advanced-stage cancer or tumors in inaccessible locations.
2. Radiation Therapy: This method can damage healthy tissues surrounding the tumor, leading to side effects such as fatigue, skin irritation, and long-term health issues.
3. Chemotherapy: Targets all rapidly multiplying cells thus, targeting both cancerous and our own healthy rapidly multiplying cells, like, blood cells, hair cells and oral and gastro-intestinal lining resulting in side effects like hair loss, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, anemia and a weakened immune system. Additionally, cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy over time. Lastly, chemotherapy medications can contribute to cancer formation at a different site.
4. Immunotherapy has less side effects but is useful only in very select patients and is very expensive.
Other than total surgical removal the cancer stem cells are able to escape other therapies and thus can lead to recurrence. Recurrence rates are, therefore, very high in any cancer that has spread beyond its original site, namely, metastases. This occurs through the blood or the lymphatics
Metabolic Therapy: A Promising Alternative
Metabolic therapy is a multi-pronged approach where six strategies are used simultaneously to target the difference in metabolism between cancer cells and our body cells. It also targets the slower growing cancer stem cells. Due to this it has few, to no side effects and in fact, strengthens our immunity. Its principal efficacy is in blocking the cancer fuel pathways thereby disrupting the cancer cell metabolism thus starving them and then killing the cancer cells. This therapy can be used synergistically with conventional cancer treatments enhancing their effectiveness and minimising their severe side-effects. Our clinic is one of the few centres in the world offering the metabolic therapy for cancer patients, an emerging area of interest in oncology. Interested readers are recommended to listen to Dr. Thomas Seyfried from the Boston Medical college on YouTube. He has done pioneering research work in the field of the metabolic therapy and is the author of the book.

Ketogenic Therapy and Cancer
One metabolic therapy involves the ketogenic diet therapy. This high-fat, low-carbohydrate and adequate protein diet shifts the body’s metabolism from relying on glucose to producing ketones from fat as a primary energy source. Cancer cells typically have high glucose uptake rates due to their increased energy demands and altered metabolism. Due to their faulty mitochondrial metabolism they are unable to use ketones as an energy source.
By restricting glucose availability, the ketogenic therapy aims to starve cancer cells while our body cells are uniquely able to thrive on ketones, and in fact, derive 50% more energy as compared to glucose.

Intermittent Fasting and Cancer
Intermittent fasting (IF) involves cycling of fasting and eating during which normal cells adapt to ketone metabolism. Research suggests that IF can reduce insulin levels, increase cellular stress resistance, improve immune function and trigger autophagy—a process where cells remove damaged components, which can inhibit cancer progression. Fasting may also enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy and reduce its side effects by selectively protecting normal cells.

Exercise and Cancer
Regular physical activity is known to boost immune function and improve overall health. Exercise has been shown to lower the risk of certain cancers and may help in reducing the side effects of cancer treatments. Mechanistically, exercise can reduce inflammation, improve immune surveillance, and regulate hormones like insulin and estrogen, which are linked to cancer development.

The Role of Sleep in Cancer Prevention and Management
Good sleep hygiene is critical for maintaining overall health and enhancing immune function. Poor sleep quality or sleep deprivation can impair the immune system, increase inflammation, and elevate stress hormone levels, all of which can contribute to cancer progression. In fact, there is a 200% increased risk of cancer in those who have less sleep. Conversely, good quality sleep can enhance immune responses, facilitate the repair of damaged tissues, and potentially improve the efficacy of cancer therapies.

Off-Label/Repurposed Drugs and supplements: Targeting Cancer Stem Cells and Metabolic Pathways
The exploration of off-label or repurposed drugs and supplements has garnered attention as a cost-effective and efficient approach to cancer treatment. These off-label drugs, originally developed for other conditions, have shown potential in targeting CSCs and blocking key metabolic energy pathways essential for cancer cell multiplication and survival. For instance, metformin, commonly used for type 2 diabetes, has demonstrated efficacy in reducing glucose availability to cancer cells, thereby inhibiting their growth. Similarly, supplements like curcumin (compound found in turmeric) have been found to have anti-inflammatory properties and interfere with cancer cell signalling pathways. By targeting glucose, glutamine, and certain fatty acids, these repurposed drugs can disrupt the energy supply to cancer cells, leading to reduced tumor growth and enhanced susceptibility to conventional treatments.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) in Cancer Treatment
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room or chamber. This therapy has been explored for its potential benefits in cancer treatment. The increased oxygen levels (form a normal concentration of 18-20% to 70-80 %) can enhance the body’s natural healing processes and improve the effectiveness of conventional therapies. Mechanistically, this increase in oxygen concentration in the blood, can induce oxidative stress in cancer cells, leading to their destruction. Typically cancer cells thrive in low oxygen milieu and can be killed by high oxygen levels. Additionally, by increasing oxygen in the tumor microenvironment, makes cancer cells more susceptible to radiation and chemotherapy. Furthermore, HBOT may promote angiogenesis (starving the cancer cells of blood supply) and enhance immune responses, contributing to its anti-cancer effects.
Cancer remains a global health challenge; with significant impacts in India and worldwide. While traditional treatments like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy have their place, they come with notable drawbacks.
Metabolic therapies, consisting of the following
- Ketogenic therapy
- Intermittent fasting
- Regular exercise
- Maintaining good sleep hygiene
- Off-label/repurposed drugs
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
They offer promising complementary strategies and are crucial for supporting the body’s natural defences and improving treatment outcomes.
If you or your loved one has cancer and is interested in exploring metabolic therapy, kindly contact our clinic for an appointment.
References:
1. [World Health Organization. Cancer](https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer)
2. [National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stem Cells](https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/research/cancer-stem-cells)
3. [Mayo Clinic. Cancer Treatment Options](https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/cancer-treatment-options)
4. [American Cancer Society. Chemotherapy Side Effects](https://www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/treatment-types/chemotherapy.html)
5. [National Library of Medicine. The Ketogenic Diet as a Treatment Paradigm for Diverse Neurological Disorders](https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25693383/)
6. [Cell Metabolism. Intermittent Fasting and Cancer](https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(18)30407-X)
7. [Journal of Clinical Oncology. Exercise and Cancer](https://ascopubs.org/doi/full/10.1200/JCO.2016.70.9223)
8. [National Institutes of Health. Metformin and Cancer](https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31710920/)
9. [Cancer Research UK. Repurposed Drugs in Cancer Treatment](https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/funding-for-researchers/our-research-priorities/research-we-fund/research-highlights/repurposed-drugs-in-cancer-treatment)
10. [National Library of Medicine. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Cancer](https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27503123/)
11. [Journal of Translational Medicine. Mechanisms of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Cancer](https://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-017-1156-4)
12. [Sleep Medicine Reviews. The Role of Sleep in Immune Function](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S108707921630042X)
13. [Nature Reviews Cancer. Circadian Disruption and Cancer](https://www.nature.com/articles/nrc3624)
